Electromagnetic clutch expansion sleeve and coupling
Electromagnetic clutch is used in the transmission system of rapier looms, air-jet looms and water-jet looms, which can realize the rapid and reliable combination, separation, power transmission, braking and positioning of active components and passive components. The clutch (picture below) is composed of four main components: brake yoke assembly 1, clutch yoke assembly 4, armature assembly 2, and rotor assembly 3. 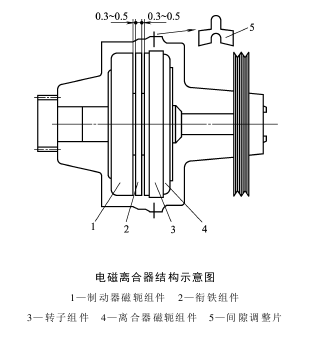 The working principle of the clutch is that when the clutch yoke is energized and the brake yoke is deenergized, the clutch yoke generates electromagnetic force By the rotor attracting the armature, a certain friction force is generated between the rotor friction plate and the armature, which realizes the reliable combination of the active part and the passive part, transmits power, and makes the loom run. When the brake is energized and the clutch is de-energized, the brake yoke generates electromagnetic force. The electromagnetic potential of the clutch yoke disappears. The armature detaches from the clutch yoke and rotor with the help of the elastic force of the spring leaf. The brake yoke attracts the armature, causing the armature and brake yoke to disengage. Friction plates generate friction. The clutch generates electromagnetic force when the magnetic yoke is energized to attract the armature. The armature and the friction plate generate friction to transmit power. Therefore, the gap between the armature and the rotor friction plate must be adjusted between 0.3 and 0.5mm. You can use the gap adjustment plate 5 (Figure 18- 1) Adjust to the best position. 1. Single-plate electromagnetic clutch The electromagnetic clutch in shuttleless looms is a special clutch within the range of single-plate electromagnetic clutch products. Its products are mainly divided into combination clutches, electromagnetic brakes, electromagnetic clutches and tooth clutches. The specifications, parameters, performance, installation dimensions, braking torque (dynamic torque), transmission torque (static torque) and other performance indicators of this type of product are all based on meeting the needs of new looms. Produced by well-known professional clutch manufacturers in Germany, Japan, and the United States, they have successfully extended the effective structure theory of multi-plate electromagnetic clutches to single-plate electromagnetic clutches dedicated to looms, improved the traditional structure of single-plate electromagnetic clutches, and perfected the clutches dedicated to looms. Structural performance greatly improves the performance of this product. For example, the armature structure has progressed from a single magnetic circuit and a single armature to a dual magnetic circuit and a single armature, and a dual magnetic circuit and a dual armature, thereby reducing the weight of the armature. On the basis of not changing the original structural dimensions of the clutch or brake, the torque of this type of product can be doubled, adapting to the demand for increased speed of shuttleless looms, and promoting the progress and efficiency of the loom. Compared with general-purpose clutches, this type of product does not come in series, is updated quickly, and will be eliminated with the update of looms. The realization of high speed, high efficiency and high reliability of modern new shuttleless looms is closely related to the development of special clutches for looms, which has become a new development category of single-chip electromagnetic clutches. Some special clutches for looms are general-purpose clutch variants, while others are specially designed for looms. No matter what type of product, they must meet the requirements of the loom for installation, debugging, maintenance, high transmission torque and high braking torque, and realize the characteristics of shuttleless looms such as quick starting and quick braking. Single-plate electromagnetic clutches and brakes, combined clutches and electrostatic actuators are all dry-type single-plate without slip rings. They have the characteristics of compact structure, fast response, long life and reliable use. They have been widely used in fabric machinery products and device. The electromagnetic clutches and brakes used in these machines and devices are mainly used as automation actuators. In order to ensure the service life of clutches and brakes, the friction plates of electromagnetic clutches and brakes, combination clutches, power-off brakes and other products must use high-performance, high-temperature-resistant non-asbestos-based friction materials. 2. Classification of electromagnetic clutches (1) Electromagnetic clutches are divided into DLD5-40 type, DLD6-160A type, DLD6-160/F type, DLD6-160/E type, DLDF-350 type and DLDF-550 type. (2) Electromagnetic brakes are divided into DZD5-80/A type, DZD5-160 type, DZD5-160/A type, DZD5-160/C type, DZD5-160/D type, DZD5-160/F type, DZD5-160A Type, DZDF-350, DZDF-550, DZDF-320/C, DZDF-320/D, DZDF-320/E, DZD5-320/X and DZD5-250/B. (3) Combined clutches are divided into DLZF-350Ⅰ type, DLZF-350Ⅱ; 450Ⅰ; 500Ⅰ type, DLZF-400 type, DLZF-450Ⅱ type, DLZF-500Ⅱ type, DLZF-500Ⅲ type, DLZF-600 type, DLZF-900 type , DLZF-900A type, DLZF-1000 type, DLZF-500ⅡA type, DLZF-850 type, DLZF-350I type, DLZF-350IV type, DLZF-1100 type and DLZF-1100A type. (4) Dog clutches are divided into DLFY-200 type, DLFY-900 type, DLFY-566 slow speed type, DLFY-566 weft-finding type and DLZF-500 type, etc. 3. Teeth electromagnetic clutch Teeth electromagnetic clutch is developed on the basis of tooth mechanical clutch. The tooth shape part is basically the same as that of tooth mechanical clutch, and there are various forms such as trapezoid, triangle, symmetrical teeth, asymmetric teeth, etc. According to the tooth shape, it can be divided into two categories: fine teeth and coarse teeth. According to the action, it can be divided into positioning teeth (unequal spacing teeth) and non-positioning teeth (symmetrical and asymmetric equidistant teeth), power-on and power-off types. Like general electromagnetic clutches, early tooth-on electromagnetic clutches were powered by slip ring brushes. Modern new tooth-on electromagnetic clutches all adopt the basic structure of a single-plate electromagnetic clutch, that is, the armature and rotor are replaced by end-face toothed discs, and the yoke is fixed The non-rotating power supply is convenient and improves the reliability of the product. The action of the tooth-engaged power-off positioning clutch is the same as that of the tooth-engaged power-off clutch, that is, it disengages when the power is on and combines when the power is off (power loss), but there is a difference.This is achieved by helping the arc-shaped surface to deform easily during work, which is more advanced than the traditional structure. There are also drum-shaped gear couplings and the middle inner gear sleeve made of organic materials with high elasticity, high strength, oil resistance, corrosion resistance and impact resistance. In order to meet the requirements of high speed, low inertia and no gap in modern mechanical transmission, diaphragm couplings and shaft connections adopt pairs of expansion rings to achieve keyless connection. The diaphragm coupling adopting this structure is more suitable for use in servo drive system transmission machinery to control the transmission gap, reduce the dead zone of the servo system, and improve the positioning accuracy and servo performance of the mechanical transmission. The expansion coupling sleeve is a new type of coupling piece that can achieve keyless coupling. The product structure of new couplings has been relatively complete, and it is combined with other transmission parts such as safety clutches to form new transmission parts products. There are many types of couplings, with more varieties and specifications. Currently, the most commonly used ones are diaphragm couplings, plum blossom couplings, drum gear couplings, cross-shaft universal couplings and expansion sleeve couplings.
The working principle of the clutch is that when the clutch yoke is energized and the brake yoke is deenergized, the clutch yoke generates electromagnetic force By the rotor attracting the armature, a certain friction force is generated between the rotor friction plate and the armature, which realizes the reliable combination of the active part and the passive part, transmits power, and makes the loom run. When the brake is energized and the clutch is de-energized, the brake yoke generates electromagnetic force. The electromagnetic potential of the clutch yoke disappears. The armature detaches from the clutch yoke and rotor with the help of the elastic force of the spring leaf. The brake yoke attracts the armature, causing the armature and brake yoke to disengage. Friction plates generate friction. The clutch generates electromagnetic force when the magnetic yoke is energized to attract the armature. The armature and the friction plate generate friction to transmit power. Therefore, the gap between the armature and the rotor friction plate must be adjusted between 0.3 and 0.5mm. You can use the gap adjustment plate 5 (Figure 18- 1) Adjust to the best position. 1. Single-plate electromagnetic clutch The electromagnetic clutch in shuttleless looms is a special clutch within the range of single-plate electromagnetic clutch products. Its products are mainly divided into combination clutches, electromagnetic brakes, electromagnetic clutches and tooth clutches. The specifications, parameters, performance, installation dimensions, braking torque (dynamic torque), transmission torque (static torque) and other performance indicators of this type of product are all based on meeting the needs of new looms. Produced by well-known professional clutch manufacturers in Germany, Japan, and the United States, they have successfully extended the effective structure theory of multi-plate electromagnetic clutches to single-plate electromagnetic clutches dedicated to looms, improved the traditional structure of single-plate electromagnetic clutches, and perfected the clutches dedicated to looms. Structural performance greatly improves the performance of this product. For example, the armature structure has progressed from a single magnetic circuit and a single armature to a dual magnetic circuit and a single armature, and a dual magnetic circuit and a dual armature, thereby reducing the weight of the armature. On the basis of not changing the original structural dimensions of the clutch or brake, the torque of this type of product can be doubled, adapting to the demand for increased speed of shuttleless looms, and promoting the progress and efficiency of the loom. Compared with general-purpose clutches, this type of product does not come in series, is updated quickly, and will be eliminated with the update of looms. The realization of high speed, high efficiency and high reliability of modern new shuttleless looms is closely related to the development of special clutches for looms, which has become a new development category of single-chip electromagnetic clutches. Some special clutches for looms are general-purpose clutch variants, while others are specially designed for looms. No matter what type of product, they must meet the requirements of the loom for installation, debugging, maintenance, high transmission torque and high braking torque, and realize the characteristics of shuttleless looms such as quick starting and quick braking. Single-plate electromagnetic clutches and brakes, combined clutches and electrostatic actuators are all dry-type single-plate without slip rings. They have the characteristics of compact structure, fast response, long life and reliable use. They have been widely used in fabric machinery products and device. The electromagnetic clutches and brakes used in these machines and devices are mainly used as automation actuators. In order to ensure the service life of clutches and brakes, the friction plates of electromagnetic clutches and brakes, combination clutches, power-off brakes and other products must use high-performance, high-temperature-resistant non-asbestos-based friction materials. 2. Classification of electromagnetic clutches (1) Electromagnetic clutches are divided into DLD5-40 type, DLD6-160A type, DLD6-160/F type, DLD6-160/E type, DLDF-350 type and DLDF-550 type. (2) Electromagnetic brakes are divided into DZD5-80/A type, DZD5-160 type, DZD5-160/A type, DZD5-160/C type, DZD5-160/D type, DZD5-160/F type, DZD5-160A Type, DZDF-350, DZDF-550, DZDF-320/C, DZDF-320/D, DZDF-320/E, DZD5-320/X and DZD5-250/B. (3) Combined clutches are divided into DLZF-350Ⅰ type, DLZF-350Ⅱ; 450Ⅰ; 500Ⅰ type, DLZF-400 type, DLZF-450Ⅱ type, DLZF-500Ⅱ type, DLZF-500Ⅲ type, DLZF-600 type, DLZF-900 type , DLZF-900A type, DLZF-1000 type, DLZF-500ⅡA type, DLZF-850 type, DLZF-350I type, DLZF-350IV type, DLZF-1100 type and DLZF-1100A type. (4) Dog clutches are divided into DLFY-200 type, DLFY-900 type, DLFY-566 slow speed type, DLFY-566 weft-finding type and DLZF-500 type, etc. 3. Teeth electromagnetic clutch Teeth electromagnetic clutch is developed on the basis of tooth mechanical clutch. The tooth shape part is basically the same as that of tooth mechanical clutch, and there are various forms such as trapezoid, triangle, symmetrical teeth, asymmetric teeth, etc. According to the tooth shape, it can be divided into two categories: fine teeth and coarse teeth. According to the action, it can be divided into positioning teeth (unequal spacing teeth) and non-positioning teeth (symmetrical and asymmetric equidistant teeth), power-on and power-off types. Like general electromagnetic clutches, early tooth-on electromagnetic clutches were powered by slip ring brushes. Modern new tooth-on electromagnetic clutches all adopt the basic structure of a single-plate electromagnetic clutch, that is, the armature and rotor are replaced by end-face toothed discs, and the yoke is fixed The non-rotating power supply is convenient and improves the reliability of the product. The action of the tooth-engaged power-off positioning clutch is the same as that of the tooth-engaged power-off clutch, that is, it disengages when the power is on and combines when the power is off (power loss), but there is a difference.This is achieved by helping the arc-shaped surface to deform easily during work, which is more advanced than the traditional structure. There are also drum-shaped gear couplings and the middle inner gear sleeve made of organic materials with high elasticity, high strength, oil resistance, corrosion resistance and impact resistance. In order to meet the requirements of high speed, low inertia and no gap in modern mechanical transmission, diaphragm couplings and shaft connections adopt pairs of expansion rings to achieve keyless connection. The diaphragm coupling adopting this structure is more suitable for use in servo drive system transmission machinery to control the transmission gap, reduce the dead zone of the servo system, and improve the positioning accuracy and servo performance of the mechanical transmission. The expansion coupling sleeve is a new type of coupling piece that can achieve keyless coupling. The product structure of new couplings has been relatively complete, and it is combined with other transmission parts such as safety clutches to form new transmission parts products. There are many types of couplings, with more varieties and specifications. Currently, the most commonly used ones are diaphragm couplings, plum blossom couplings, drum gear couplings, cross-shaft universal couplings and expansion sleeve couplings.
AAAFGHTYHCGER
Disclaimer:
Disclaimer: Some of the texts, pictures, audios, and videos of some articles published on this site are from the Internet and do not represent the views of this site. The copyrights belong to the original authors. If you find that the information reproduced on this website infringes upon your rights, please contact us and we will change or delete it as soon as possible.
AA




