Yarn (8): The structure of yarn
Many people have misunderstandings or understanding of “Yarn (8): The Structure of Yarn“. Next, let me take you with me to share it with your friends and explore more about ” Yarn Chapter 8: The Structure of Yarn” knowledge…
1. Basic structural characteristics of spinning yarn
Requirements for spinning yarn structure: uniformity of appearance, continuity of intrinsic composition quality and distribution, and stability of interaction between fibers.
Decision-making factors: fiber arrangement, packing density and interaction between fibers.
After the spun yarn is twisted, the outer layer is tightened, the inner layer shrinks, the fibers are tilted, and the length of the spun yarn is shortened.
The axial shrinkage force generated by the elongation tension of the outer fiber forces the fiber to move inside and outside the spinning yarn.
2. Structural characteristics of commonly used spinning yarns
(1) Staple fiber yarn and laminate yarn
1. Ring-spun yarn
1) The basic structural feature is tight inside and loose outside;
2) Half of the fibers are in the form of conical spirals; a small part of the fibers do not transfer internally or externally and are in the form of cylindrical spirals;
3) A small part of the fibers are in the form of hooks, loops, folds, etc.;
4) Most fiber head ends are exposed to form hairiness, and a few head ends are bent, shrunk or wrapped around other fibers.

2. Free end yarn
1) The internal and external transfer of fibers is not significant, and most fibers are in the form of cylindrical spirals.
2) The fiber straightness in the yarn is low, and the number of hooked, looped, and folded fibers is large;
3) Rotor spinning is loose inside and tight outside, with multiple wrapped fibers in the outer layer and high fiber orientation in the inner layer;
4) The surface of the free-end yarn is rough, with poor luster and hard feel, but the evenness is good.
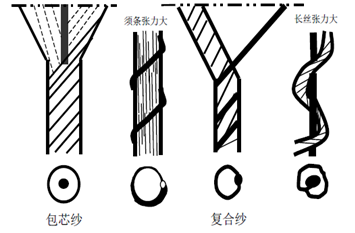
3. Structural characteristics of laminated yarns and structural yarns
The structural characteristics of the laminated yarn are determined by its length/short, short/short, long/long fitting ratio and tension. This structure can effectively improve the yarn strength and increase the continuity and stability of the yarn.
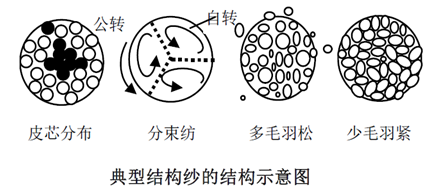
The structural characteristics of structural yarn are determined by its fiber distribution pattern and aggregation density.
(2) Structural characteristics of filament yarn
1. Structural characteristics of untwisted filament yarn
The lateral structure is extremely unstable and soft.
2. Structural characteristics of twisted filament yarn
It is very stable and stiff vertically and horizontally.
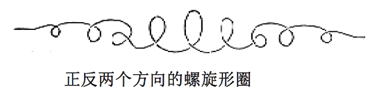
3. Structural characteristics of textured yarn
Different finishing methods have different curling shapes, such as spiral, wavy, zigzag, loop, etc. The packing density and arrangement and distribution are also different.



(3) Structural characteristics of strands
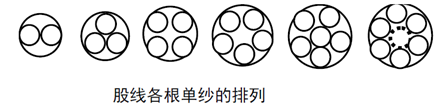
When the number of single yarns twisted at one time is within 3, the strand structure is stable; 4 to 5 yarns have instability factors, and 6 or more yarns must return to the stable state of 3 yarns.
When the twist directions of single yarn and strand are opposite, the twist is stable and the strand structure is uniform and stable. Spinning yarn (8): The structure of spinning yarn
AAASDFWERTEYRHF
Through the above description of “Yarn Chapter 8: The Structure of Yarn“, you will have a better understanding of “Yarn Chapter 8: The Structure of Yarn” What is your understanding and idea of ”structure“, or if you are interested in purchasing fabrics, you are welcome to leave your comments below on the website!
Disclaimer:
Disclaimer: Some of the texts, pictures, audios, and videos of some articles published on this site are from the Internet and do not represent the views of this site. The copyrights belong to the original authors. If you find that the information reproduced on this website infringes upon your rights and interests, please contact us and we will change or delete it as soon as possible.
AA





