Yarn (7): Yarn processing and development
Many people have misunderstandings or understanding of “Yarn (7): Yarn Processing and Development“. Let me take you with me to share and explore with your friends. Knowledge about “Yarn Part 7: Yarn Processing and Development“…
1. Basic principles of spinning yarn finishing
Finishing of staple fiber yarn
Fiber opening (impurity removal and mixing) – carding into web – strip forming – drawing and mixing – drafting and twisting – yarn forming – package forming
Finishing of filament yarn
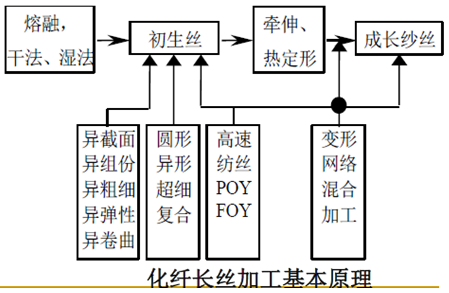
Cord arrangement
Thread forming: yarn or silk, or yarn-silk are twisted and combined together. The basic process is: tension pre-control-merging-twisting-packing.
Rope is a special variety in the fabric industry, which is made of multiple strands of yarn or threads twisted together.
2. Progress in spinning yarn finishing
1. Progress in yarn finishing technology
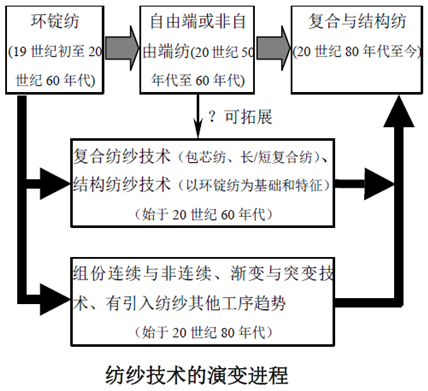
(1) Open end spinning
Separate the fibers into individual fibers and condense them, then twist them into yarn without mechanical holding at one end.
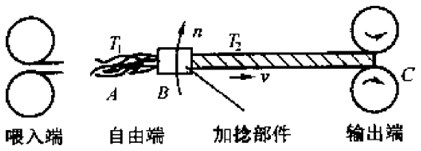
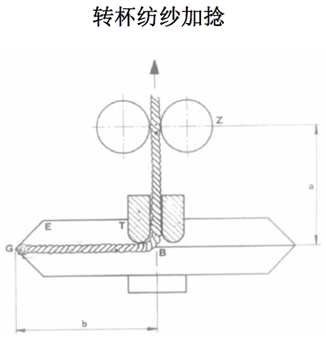
①Rotor yarn (or rotor spinning)
The negative pressure airflow in the rotor is used to transport fibers and the high-speed rotation of the rotor condenses the fibers and twists them into yarn. Suitable for spinning 18-100tex pure cotton yarn, wool yarn, linen yarn or blended chemical fiber fabric yarn with chemical fiber.
②Electrostatic yarn
Using high-voltage electrostatic fields to polarize fibers and condense them into whiskers, they are made by twisting hollow tubes running at high speed.
③Vortex yarn
A yarn made by twisting the shavings using the rotating airflow of the vortex. Suitable for spinning 60-100tex chemical fiber yarn or blended chemical fiber fabric yarn, mostly used as pile yarn
④Friction spinning
The negative pressure airflow in the dust cage is used to absorb fibers and the rotation of the dust cage causes friction and twisting of the whiskers into yarn. Widely used in carpets, interlinings and thick decorative fabrics.
(2) Self-twisting yarn
The two strands are twisted in the same direction by the reciprocating movement of the rubbing roller, and are rewinded together by the untwisting torque of the strands themselves to form a double-stranded yarn with a stable structure, which is a non-free-end spinning yarn.
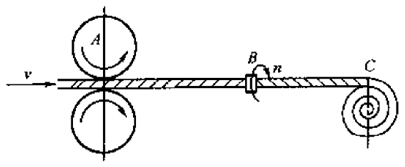
(3) Core-spun yarn
Yarn with a wrapping structure with filament as core and short fiber as skin is a laminating yarn. It can be realized on ring spinning machines or twisting machines, rotor spinning, vortex spinning, dust cage spinning, and self-twisting spinning.
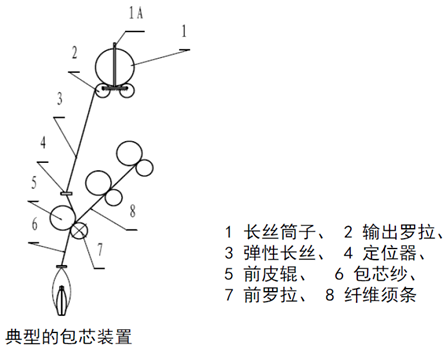
(4) Air-jet yarn
The rotating airflow in the nozzle is used to falsely twist the slivers, and the free fibers at the head end are wrapped around the untwisted short fiber yarn core to form yarn. The strength is lower than ring-spun yarn, the diameter is slightly thicker, and the outer fiber has obvious directionality.

(5) Twisted yarn and bonded yarn
The molten polymer or the filament and short fiber adhered to the molten resin are used to pass through a pair of rollers. The short fiber is wrapped around the polymer filament. In the semi-molten state, it is twisted with air flow and cooled. Get yarn.
The short fiber bonding yarn is untwisted yarn.
(6) New laminated structural yarn
Mainly refers to laminated yarns twisted into short/short and short/long fibers on ring spinning machines and yarns obtained through single sliver splitting or sliver aggregation.
①Sirospun
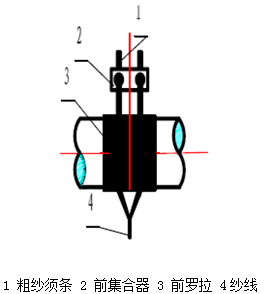
Principle: Two rovings are introduced into the drafting area of the spinning machine in parallel at a certain distance, drafted at the same time, and twisted together in the bundling triangle area to form a single yarn. Both the sliver and the yarn have the same twist.
Features: Wired features, relatively clean surface, less hairiness, loose inside and tight outside, good elasticity and high wear resistance.
②Sirofilyarn
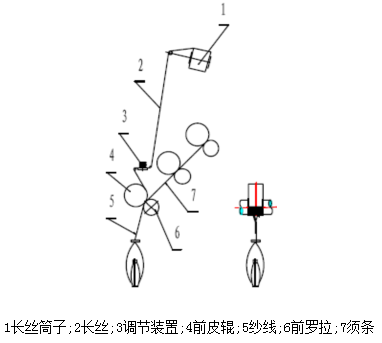
Principle: A laminated yarn is formed by laminating and twisting a drafted sliver and a multifilament that has not been drafted but has a certain tension in the twisting triangle area.
Features: The appearance is like a single yarn, the structure is like a thread, the surface hairiness is less than that of ring-spun yarn, and the cross-section is approximately circular.
③Solospun or cable spinning

Principle: The fiber strands are split into 3 to 5 small bundles through grooves and front rollers, thereby changing the twisting and transfer mechanism of spinning. separate fibers�The bundles may be twisted before converging and twisted again at the converging point.
Characteristics: less hairiness, clean surface, high strength and good wear resistance.

④Concentrated spinning (compactyarn)

A pair of gathering rollers are installed at the front roller of the ring spinning machine where the whiskers are output. Among them, the bottom roller has the function of suction and gathering, so that the whiskers are clustered in the pneumatic gathering area. The whiskers are arranged more closely, which can reduce the traditional processing speed. The width of the sliver in the twist triangle area is conducive to reliably twisting the fibers in the sliver into the yarn sliver, thereby reducing hairiness.

2. Progress in silk finishing
(1) Deformation finishing
①Thermal (mechanical) deformation method: represented by the false twist deformation method
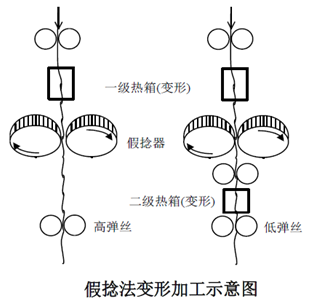
②Air deformation method:
Air textured yarn: Overfeed the slightly twisted filament bundle into the high-pressure air jet head. Due to the impact of the jet, the fibers in the filament bundle are disordered and generate rings of different sizes, which are twisted back and clamped in the filament bundle to form yarn. .
Network filament: The filament bundles are dispersed into single filaments under the impact of vertical airflow, and are intertwined and tangled at a certain distance to form relatively loose filaments.
③Combined yarn method
Fibers with two different shrinkage rates are spun into yarn and placed in steam, hot air or boiling water. The high shrinkage fiber shrinks when exposed to heat, and the low shrinkage fiber is stretched and bent. The entire yarn becomes loose, such as polyester. Acrylic fiber bulked yarn.
(2) Modification and finishing of silk
Including surface modification of silk, impregnation, plating, PU coating treatment and splitting, peeling treatment, as well as oxidation and carbonization treatment.
3. Progress of line finishing
The thread itself is a multi-axis laminate, so the progress of thread finishing is mainly reflected in changes in appearance and performance, giving functionality and moving closer to fabrics and finished products.
AAAGFREGRTTHR
Through the above description of “Yarn Chapter 7: Yarn Processing and Development“, you will know about “Yarn Chapter 7): Yarn What are your understanding and thoughts on “Thread Processing and Development“, or if you are interested in purchasing fabrics, you are welcome to post your comments below the website!
Disclaimer:
Disclaimer: Some of the texts, pictures, audios, and videos of some articles published on this site are from the Internet and do not represent the views of this site. The copyrights belong to the original authors. If you find that the information reproduced on this website infringes upon your rights and interests, please contact us and we will change or delete it as soon as possible.
AA





